Key takeaways
- Supply chain automation uses technology to replace manual processes like inventory tracking, order fulfillment, and procurement coordination.
- Common automation tools include inventory management software, barcode scanning, and automated picking/packing systems.
- Automation benefits include fewer errors, real-time production visibility, smoother workflows, and the ability to scale without sacrificing service quality.
- Implementation challenges like budget constraints, integration issues, staff resistance, and poor rollout planning can derail automation efforts if not addressed early.
- Emerging trends such as AI-driven forecasting and IoT sensors are shaping the future of automation, enabling predictive decision-making and proactive supply chain management.
If you manage logistics, distribution, or procurement, you’ve probably faced the challenge of keeping operations flowing smoothly. That’s where supply chain automation steps in. It’s the use of technology to simplify and streamline tasks that were once handled manually, from tracking inventory to coordinating deliveries.
Instead of relying on spreadsheets or endless emails, supply chain automation replaces repetitive labor with intelligent systems. These tools speed things up and reduce costly errors that slow your business down. Automation is now transforming every phase of the supply process, from procurement to fulfillment, so your team can operate with better speed and clarity.
This article explores how supply chain automation works, what tools make it possible, and how to start implementing it in a way that drives real results.
Key components of supply automation
Getting started with automation doesn’t mean jumping straight into robots or artificial intelligence (AI). At its core, supply automation begins with practical tools you can put to work right away.
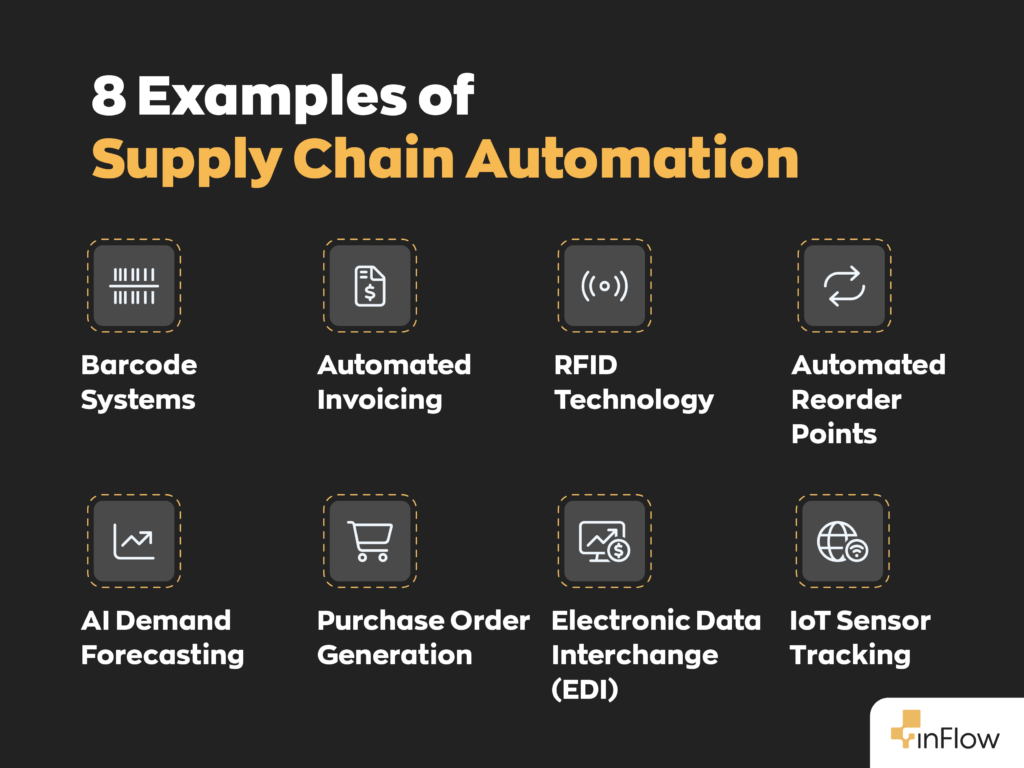
For many businesses, the first step is adopting inventory management software that centralizes stock levels, order statuses, and supplier details in one dashboard. A good system helps you know what you have, where it’s stored, and when it’s time to reorder — all without digging through piles of paperwork.
Barcoding systems and automated picking solutions also play key roles. These tools help warehouse staff locate, scan, and ship items faster with fewer mistakes. Automated fulfillment systems go further by connecting your online orders directly to your warehouse, so everything from packaging to shipping can run without manual input.
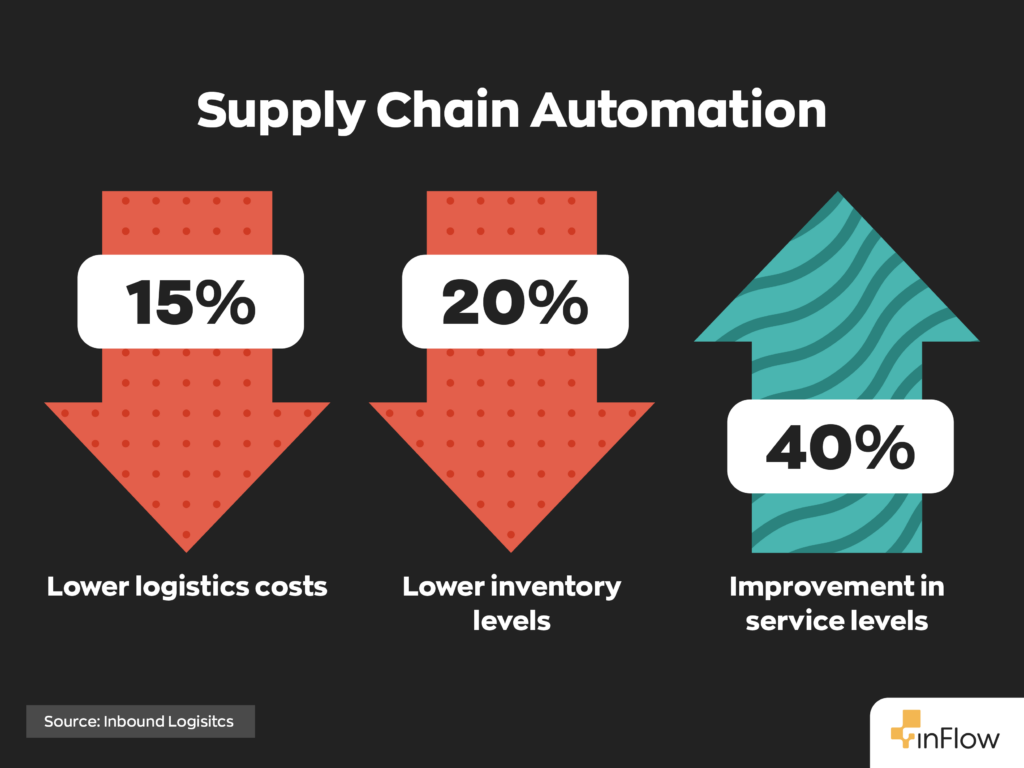
Benefits of automation in supply chain operations
Every efficiency gain matters when you’re constantly managing moving parts, inventory, orders, suppliers, and shipping. Below are some of the most impactful ways automation can improve your work across warehousing, procurement, and fulfillment.
Improved accuracy and speed
Human error is one of the biggest challenges in supply chain management. Whether it’s incorrect stock counts or shipping delays, these mistakes can damage customer relationships and increase costs. Automation minimizes those risks. With digital systems handling repetitive tasks, you get faster execution and fewer mistakes.
Real-time production tracking
Manufacturers benefit from automation tools that keep their production lines on schedule. Manufacturing software platforms allow you to track raw materials and production timelines in real time, reducing guesswork and giving your team a clearer view of operations from start to finish.

Fewer bottlenecks
You can shorten the time between purchase and delivery by automating fulfillment steps, from receiving an order to shipping it out. This gives customers a smoother experience and frees your team to focus on higher-level strategy instead of getting bogged down in routine logistics.
Automated inventory management brings more than just convenience; it builds a foundation of consistency. When your operations run smoothly and predictably, you have more room to scale, take on new clients, and respond quickly to demand shifts without sacrificing accuracy or service.
Common challenges in supply automation
Though the payoff of supply chain automation can be significant, getting there isn’t always simple. Automation introduces new systems, changes to workflows, and sometimes unexpected growing pains. To avoid frustration and failed investments, it helps to know what hurdles you might face along the way and how to prepare for them.
Budget limitations
Cost is one of the first barriers businesses encounter. Upgrading from manual processes to advanced systems can require a sizable upfront investment. You’ll need to invest in inventory management software and new hardware like barcode scanners — and spend time training your staff on how to use them.
Integration issues
Your current systems, whether for finance, shipping, or customer service, might not easily mesh with the automation tools you’re considering. Without proper integration planning, you can end up with a messy tech stack that creates silos instead of improving communication.

Change resistance and training gaps
People are creatures of habit. Even if a new tool offers clear benefits, some team members may resist change and not want to adopt it. Training is critical, but so is communicating the value of automation clearly and consistently across departments.
Poor implementation can introduce risk
A rushed or poorly planned rollout can do more harm than good. Incomplete workflows, lack of contingency plans, or overdependence on one tool can all lead to disruptions. In fact, when automation is handled without oversight, it can introduce operational risks that are harder to detect and fix.
Recognizing these challenges early gives you a chance to overcome them, if not prevent them from happening in the first place. With a clear plan and strong support from leadership, you’ll be better equipped to roll out automation that supports your team.
How to start automating your supply chain
Starting small can make the automation journey more manageable. To get started, identify the tasks that are the most time-consuming and error-prone in your current workflow. For many businesses, that means tackling inventory tracking first.
Switching from manual stock counts to a digital system helps you get a clearer view of what’s coming in and going out. From there, look for tools that fit your specific needs. If you’re managing bulk purchases and need to keep tabs on hundreds of SKUs, wholesale software for inventory and order management can help you stay organized and responsive.
Once you’ve seen the benefits in one area, expanding automation across other touchpoints — like order fulfillment, supplier communication, or delivery tracking — becomes easier. The key is to make gradual, well-supported improvements instead of automating everything simultaneously.
Monitoring and optimizing supply chain automation
Automation isn’t a one-and-done process. You’ll need to monitor how your systems are performing and where you can improve. Dashboards, reports, and performance metrics will become your best friends here.
Track order accuracy rates, turnaround times, and stock levels regularly. These insights will help you fine-tune operations and avoid common pitfalls like overordering or missed reorder points. Integrated analytics tools also let you optimize how you work with vendors and adjust supply levels before problems crop up.
More importantly, performance tracking gives your team real-time data to work with. That level of visibility allows your team to make better decisions, solve problems more quickly, and collaborate smoothly across other departments in your organization.
Future trends in automation in supply chain management
The future of supply chain automation is already taking shape, and it’s being built with smart, connected systems. AI and machine learning are powering smarter forecasting and demand forecasting. That means you can predict supply needs based on seasonal trends, market conditions, or even weather data.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is also transforming how goods are tracked in transit. Sensors can now monitor temperature, humidity, or location in real time, helping ensure sensitive products arrive in good condition.
Businesses that embrace these technologies early are setting themselves up to build more resilient, flexible supply chains. Instead of reacting to disruptions, they can respond proactively and maintain continuity, even during a crisis. If you’re not exploring how automation can work for your business, you’re likely leaving efficiency and profit on the table.




0 Comments