Key takeaways
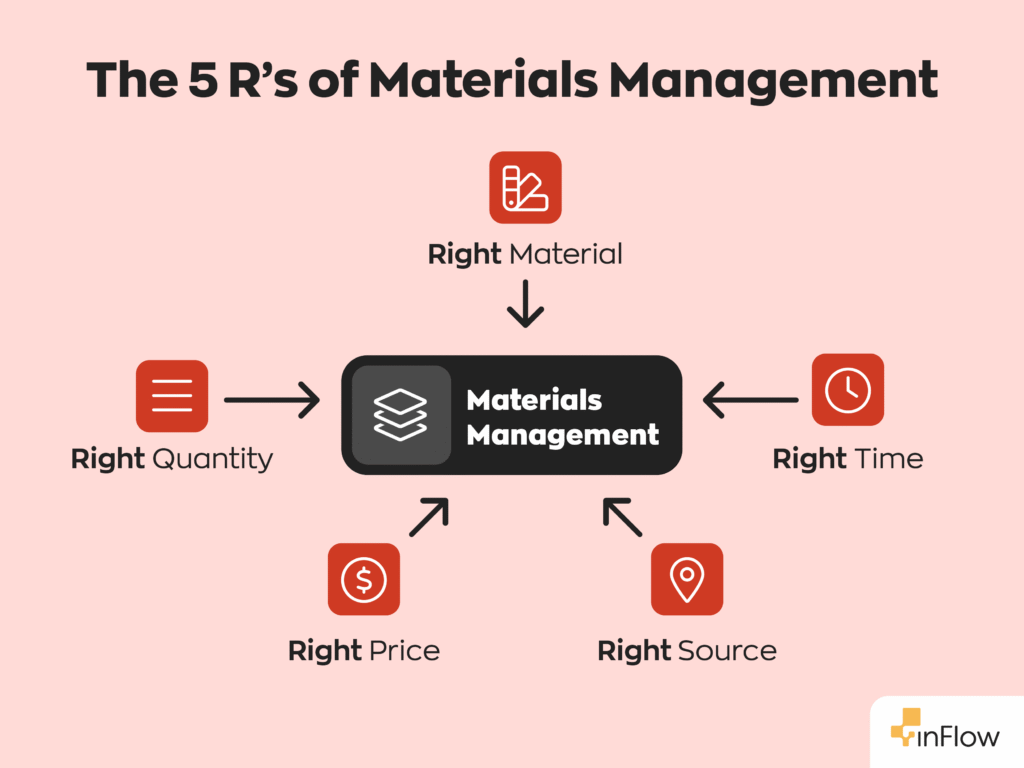
- At its core, materials management involves securing the right materials, in the right quantity, at the right time, for the right price, and from the right source.
- Effective materials management helps prevent shortages, reduces waste, strengthens supplier relationships, and enhances overall operational efficiency.
- Tools like MRP, ERP, and WMS systems enable data-driven decision-making, real-time tracking, and automation, leading to smarter operations.
- Common challenges include inaccurate data, supplier delays, and storage limitations.
- Implementing a robust materials management system improves cost control, sustainability, and customer satisfaction.
Here’s a number that might surprise you: the United States used 7.8 gigatons of materials in 2019. That’s 34% more than in 1970, according to the Center for Sustainable Systems. With numbers like that, it’s easy to see why materials management is crucial for businesses nationwide.
So, what exactly is materials management? Simply put, it’s about getting the right materials to the right place at the right time, and in the right quantities. It can be a bit of a juggling act, but when done right, effective materials management can transform your operations. We’re talking streamlined workflows, reduced waste, and the kind of cost efficiency that will increase your bottom line.
So without further ado, let’s dive into what materials management can do for your business.
What is material management? Understanding the scope
At its core, material management encompasses everything related to the flow of materials in an organization, including:
- Procurement
- Planning
- Storage
- Internal movement
- Distribution
Material management is more strategic than inventory management, and isn’t just about tracking stock levels.
Here’s what effective material management includes:
- Balancing demand and supply.
- Preventing bottlenecks.
- Creating stronger relationships between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors.
Its scope stretches from raw material acquisition all the way to the final delivery of finished products, highlighting its central role in supply chain success.
For example, imagine a popular local restaurant heading into a busy weekend. Without a strong materials management strategy, the owner might guess their ingredient needs. In doing so, they could easily over-order perishable items like fresh avocados or fish, leading directly to spoilage that cuts into their profit margins.
On the other hand, under-ordering a key ingredient could mean selling out of their signature dish on a packed Friday night, resulting in disappointed customers and lost revenue. Proper materials management uses forecasting and sales data to ensure the right quantity of the right ingredients arrive at the right time, minimizing waste and keeping customers happy.
Key functions of materials management
The functions of materials management are diverse, yet interconnected. Together, they create a framework that supports operational efficiency and reduces risks.
1. Material planning: the foundation of operational efficiency
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and warehouse management systems are used for material planning, ensuring that production has the necessary inputs when needed.
Accurate planning helps companies:
- Prevent shortages that can halt production.
- Avoid overstocking, which ties up capital and storage space.
- Respond to changes in market demand quickly.
2. Procurement and purchasing: acquiring what’s needed, when it’s needed
Procurement is about more than just buying goods; it’s about strategic sourcing. Materials management ensures that purchases align with production needs, quality requirements, and cost targets, which involves:
- Managing supplier relationships to secure reliable partnerships.
- Issuing purchase orders at the right time to avoid delays.
- Negotiating favorable pricing and delivery terms.
- Ensuring compliance with quality standards.

3. Storage and warehousing: managing inventory between steps
Materials management emphasizes organized storage systems, proper labeling, and safe handling of goods.
Best practices in warehousing include:
- Implementing FIFO (First In, First Out) or LIFO (Last In, First Out) methods, depending on material type.
- Designing efficient layouts to minimize travel time.
- Using warehouse management systems (WMS) for real-time tracking.
Avoid excess inventory as much as possible. Overstocking can lead to material degradation, increased overhead, and inefficiency. It also results in losses when the excess stock turns to dead stock for one reason or another.
4. Material movement: tracking internal flow and external logistics
With materials management, you also track the movement of all goods, not only within the organization, but also across external supply chains, including:
- Inbound logistics (supplier to warehouse).
- Internal handling (warehouse to production line).
- Outbound logistics (finished goods to customers).
Efficient material movement reduces bottlenecks, improves safety, and enhances customer satisfaction through timely deliveries, which play a huge role in customer retention and building customer trust and loyalty.
How materials management supports supply chain optimization
A well-executed materials management strategy ensures that every part of the supply chain works efficiently. Benefits include:
- Reducing lead times by aligning procurement and production schedules.
- Minimizing costs through accurate demand forecasting.
- Enhancing collaboration with suppliers and distributors.
- Improving customer service with faster and more reliable delivery.
By eliminating inefficiencies, businesses can gain a competitive edge in the market.
Materials management vs inventory management: what’s the difference?
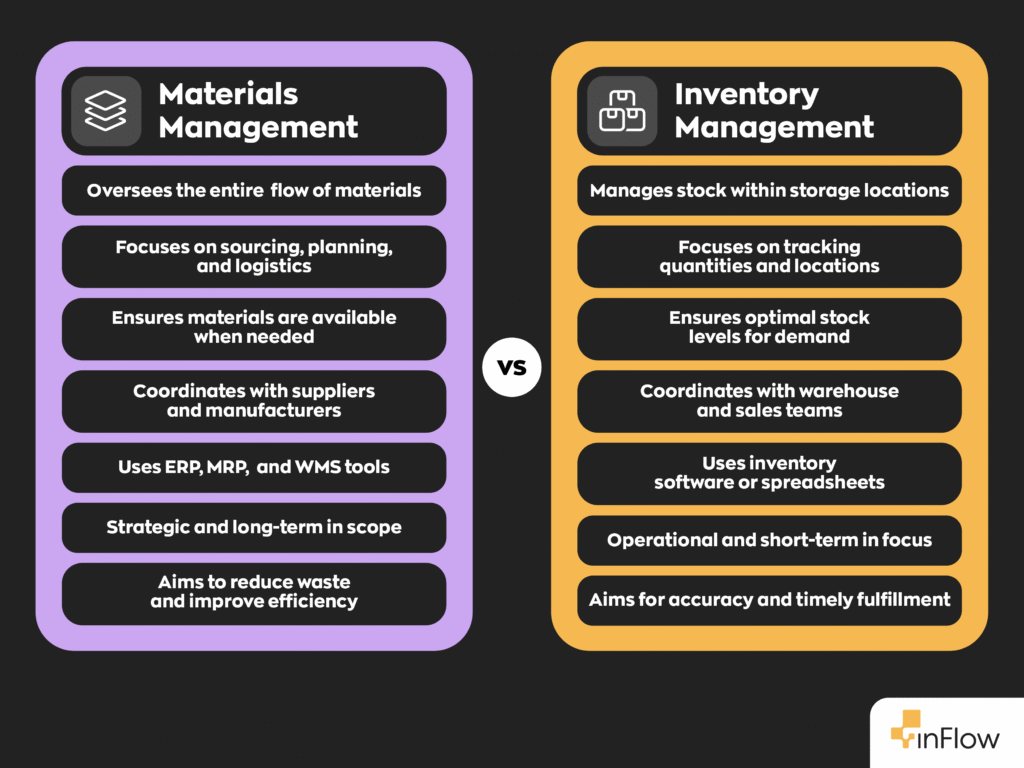
As mentioned previously, materials management and inventory management aren’t the same thing. Many people use them interchangeably, but wrongly so.
- Inventory management focuses on monitoring stock levels, recording usage, and ensuring replenishment.
- Materials management takes a broader view, encompassing procurement, planning, storage, movement, and coordination with the overall supply chain.
Inventory management, technically speaking, is a subset of materials management, the latter being more strategic.
Benefits of strong materials management systems
Organizations that invest in effective materials management enjoy multiple benefits. These include:
- Cost savings: Reduced waste, fewer stockouts, and optimized purchasing.
- Efficiency: Streamlined operations and fewer production delays.
- Sustainability: Reduced material waste and improved use of resources.
- Better supplier relationships: Consistent communication and collaboration improve trust and reliability.
- Improved decision-making: Data-driven insights help leaders respond quickly to changes in demand or supply chain disruptions.
Are you taking advantage of all these benefits using a material management software system?
Common challenges and how to overcome them
Despite its benefits, materials management comes with challenges:
- Inaccurate data: Errors in forecasting can cause shortages or excess inventory.
- Solution: Implement robust tracking systems and data analytics.
- Supplier delays: Late deliveries can halt production.
- Solution: Diversify suppliers and maintain safety stock.
- Storage limitations: Poorly managed warehouses result in decreased efficiency.
- Solution: Use WMS software and optimize storage layouts.
- High costs: Procurement inefficiencies or wastage can inflate expenses.
- Solution: Negotiate long-term supplier contracts and adopt lean inventory practices.
By addressing these challenges proactively, companies can achieve smoother operations.
Tools and technologies for smarter materials management
Advancements in technology have transformed how businesses handle materials management. Some key tools include:
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems: Integrate financial, procurement, and production processes.
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP): Forecasts and plans material needs
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): Track real-time inventory and optimize storage.
- Automation and Analytics: Robotics, AI, and predictive analytics improve accuracy and efficiency.
These tools allow businesses to gain real-time visibility, minimize errors, and make smarter, data-driven decisions.

FAQs
What are the 5 R’s of material management?
The 5 R’s are: getting the right material, in the right quantity, at the right time, at the right price, and from the right source.
What does a materials manager do?
A materials manager oversees procurement, inventory, storage, and distribution to ensure resources are available when needed without overstocking.
Supply chain optimization begins with materials management
At inFlow, we make the inventory component of your strategy simple and powerful. Our software is designed for small to mid-sized businesses, handling everything from sales and shipping to barcoding and reporting.
50k+ businesses are using inFlow inventory (GDPR and SOC 2 compliant) to smooth out their supply chain. What are you waiting for? Find out if our inventory management software is right for you. Book a 15-minute call to get our honest opinion.





0 Comments